Unknown Medical Conditions That May Impede Weight Loss
Losing weight can be challenging for you, and several factors can make it even harder. One of the most significant factors is having an underlying medical condition that affects your metabolism, hormonal balance, or appetite control. This article explores ten of these medical conditions in more detail.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a common medical condition in which the thyroid, a small gland at the base of your throat, does not produce enough hormones. This can make it difficult for your body to control its metabolism, which makes it more challenging to lose weight.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, unexplained weight gain, constipation and dry skin. If you have any of these symptoms and cannot lose weight despite making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthier diet or exercising more regularly, talk to your doctor.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)

Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by the presence of numerous small cysts on the ovaries, which can cause hormonal imbalances and lead to problems with fertility, metabolism, and weight gain.
The symptoms include irregular periods, acne, excessive hair growth, and difficulty losing weight. Women with PCOS may also experience depression or anxiety due to their symptoms. With proper medical treatment and lifestyle modifications such as exercise and healthy eating habits, many of these symptoms can be managed.
Cushing’s Syndrome

Cushing’s Syndrome is a rare hormonal disorder caused by abnormally high cortisol levels in the body. High cortisol levels can cause weight gain, particularly in the face, neck, and abdomen. It is often related to taking certain medications, such as corticosteroids, or having tumors on the adrenal glands.
Symptoms of Cushing’s Syndrome include changes in skin texture (thinning), easy bruising, depression or anxiety, and difficulty losing weight. Treatment for this condition typically involves reducing cortisol levels through medication or surgery.
Diabetes
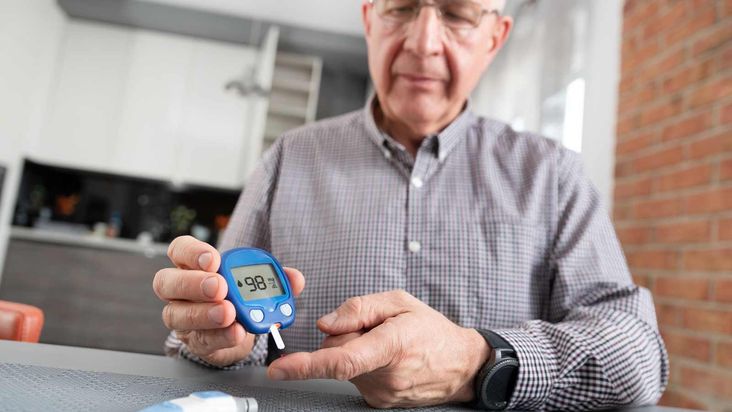

Diabetes is a chronic condition that prevents the body from producing or using insulin correctly. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the blood instead of being used for energy. Symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores or cuts.
Diabetes is typically managed with lifestyle changes (diet and exercise) as well as medications. In some cases, insulin injections may be needed to control blood sugar levels.
Obesity

Obesity is having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher. Many factors, including genetics, lack of physical activity, and unhealthy eating habits, can cause obesity. This condition increases your risk for severe medical conditions including heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Obesity makes it more challenging to lose weight due to several factors, including the body’s resistance to weight loss, hormonal imbalances, and increased appetite. Treatment involves changing lifestyle habits to promote healthy eating and regular exercise.
Sleep Apnea
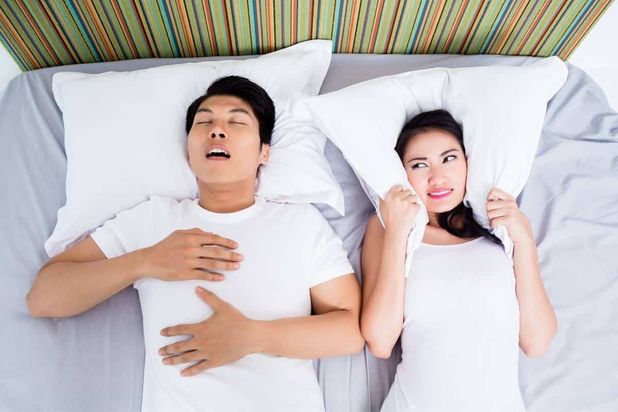

Sleep apnea is a disorder in which breathing stops and starts during sleep. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including being overweight, having large tonsils or adenoids, or other physical structural changes that block the airway.
Sleep apnea symptoms include loud snoring, disturbed sleep, and headaches in the morning. How does apnea affect weight loss? The hormonal imbalance that results from sleep apnea can impede your weight loss goals, as well as cause excessive daytime fatigue which can make it difficult to exercise or stick to a healthy diet.
Depression

Depression is a serious mental health disorder that can affect many aspects of your life, including eating and exercise habits. People with depression often have difficulty sleeping, lack energy and motivation, and may not feel like getting up to exercise or grocery shop for healthy food items.
Furthermore, individuals with depression are more likely to turn to “comfort foods” such as high-calorie snacks and fast food, which can lead to weight gain. If you are struggling with depression, seek professional help so that you can develop effective coping strategies for dealing with your symptoms.
Metabolic Syndrome

Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that increase your risk for serious health problems such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes. It is associated with having an unhealthy lifestyle and being overweight or obese. The symptoms include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and excess abdominal fat.
Treatment for metabolic syndrome involves changing your diet and exercise habits. Medication may also be prescribed to help control the other symptoms of this condition.
Gastrointestinal Issues

Gastrointestinal conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and Crohn’s disease can make it harder to lose weight due to the chronic inflammation and abdominal pain they cause. These conditions can also lead to loss of appetite or malabsorption of nutrients, affecting your ability to get adequate nutrition from food.
If you have signs of a gastrointestinal issue such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, or constipation, talk to your doctor for evaluation and treatment. Treatment may involve medications and dietary changes to help manage symptoms and promote healthy digestion.
Hypogonadism

Hypogonadism is when the reproductive glands do not produce enough hormones. This condition can lead to hormonal imbalances, affecting metabolism and making it harder to lose weight. It is more common in men than women and is usually diagnosed between ages 30-50.
The symptoms of hypogonadism include fatigue, loss of muscle mass, erectile dysfunction, hot flashes, and changes in mood or behavior. Treatment typically involves taking prescription hormones or undergoing testosterone replacement therapy.