10 Skin Rashes That are Common and Ways to Eliminate Them
Most people will have a skin rash at some point in their lives. Identifying the signs of certain skin disorders, such as eczema and measles, can help you seek appropriate care.
While most rashes are not serious, some can be dangerous and require immediate medical attention. This article uncovers the most common skin rashes, including their causes, symptoms, and treatments.
1. Eczema

Eczema is a non-contagious skin rash without a cure, but by taking medication or avoiding irritants, symptoms can be managed. Kids who suffer from eczema may outgrow it on or before their 10th birthday. However, others may continue to experience symptoms at different points in their lives.
What Causes Eczema?
Eczema is a common skin condition that results from inflammation of the skin. Irritants like soaps, fragrances, harsh detergents, and environmental pollutants most commonly cause it.
Allergens such as pollen and mold can also trigger eczema flare-ups. Other factors that may contribute to the condition include dry skin, stress, genetics, and hormonal imbalances.
How Is Eczema Diagnosed?
Eczema is usually diagnosed based on a physical examination of the skin. Your doctor may ask about your medical history and have you describe any symptoms you have been experiencing. In some cases, your doctor may order a biopsy or other tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Eczema Treatment
Since eczema comes with itchy sensations, the recommended treatment may focus more on preventing itching. Your doctor may also recommend body lotions and creams to keep your dry and itchy skin moist. Hydrocortisone cream and antihistamine have been known to be helpful.
2. Diaper Rash

This is a type of contact dermatitis in which there is an inflammation of the skin in the area of the body covered by a diaper. The irritants responsible for this skin disorder are urine, faeces… leading to the breakdown of the skin.
Diaper rash is most common in the first 2 years of life. However, anyone who routinely wears diapers can also be affected.
What Causes Diaper Rash?
• Infrequent diaper changes
• Irritants such as soaps, detergents, or creams applied to the skin
• Prolonged contact with urine or feces
• Yeast infection
• Allergic reaction to certain foods in the baby’s diet
• Sensitivities to certain diaper materials or fragrances.
Diagnosis Of Diaper Rash
Diagnosing diaper rash usually requires a physical examination of the skin in the affected area. Your doctor may ask about any recent changes in diet, hygiene habits, or skin care products used by your baby.
Your doctor can also take a sample of the rash to test for bacteria, fungus, and other causes that might be irritating.
Diaper Rash Treatment
The medical doctor may prescribe topical creams and ointments to treat diaper rash. These creams and ointments include:
- Hydrocortisone to reduce swelling.
- Zinc oxide
- Antifungal creams
3. Chickenpox
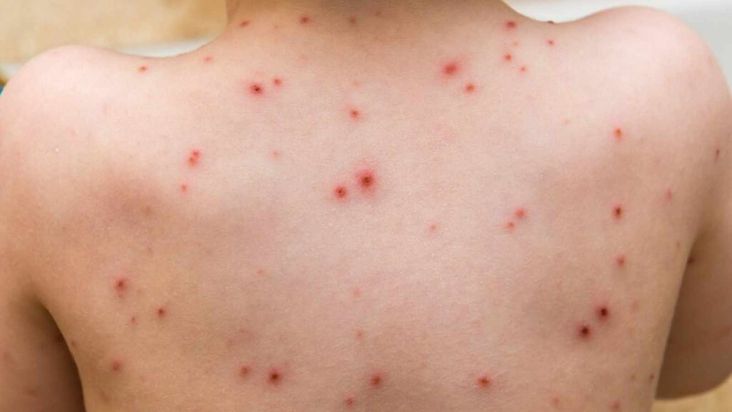
Chickenpox is a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It’s characterized by an itchy, blister-like rash that can spread over your body.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include fever, headache, loss of appetite, fatigue, and swollen glands. Complications from chickenpox can be severe, so it is vital to seek medical attention if you or your child has been exposed to the virus.
People who haven’t suffered from chickenpox or who haven’t been vaccinated against the disease are more susceptible to contracting it.
What Causes Chickenpox?
• Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which is part of the herpesvirus family
• It usually spreads through direct contact with an infected person’s respiratory secretions, such as saliva or mucus
• It can also spread through contact with their blister fluid or contaminated objects, such as bedding, clothing and toys
How Is Chickenpox Diagnosed?
Chickenpox is usually diagnosed based on a physical examination and the patient’s history of symptoms. A laboratory test may also be performed to detect antibodies in the blood that indicate chickenpox infection.
Chickenpox Treatment
Chickenpox treatment generally focuses on relieving symptoms and helping to prevent secondary infections. Treatment may include:
• Taking a pain reliever or antipyretic to reduce fever and discomfort
• Applying calamine lotion, baking soda baths, or cool compresses to help relieve itching
• Taking an antihistamine to reduce itchiness
• Practicing good hygiene to avoid the spread of infection
• Getting plenty of rest
4. Scabies

Scabies is an infestation caused by a tiny mite that burrows beneath the skin. It is spread through close physical contact, such as sleeping in the same bed or having sex.
Itching and bumps on the skin are usually the first signs of scabies. Other symptoms include thin gray lines on the skin, often found between fingers and toes, and a pimple-like rash.
What Causes Scabies?
Scabies is primarily caused by human contact with an infected person. The mites that cause scabies can survive for up to 72 hours outside the human body and spread through skin-to-skin contact or contact with contaminated objects, such as clothing, bedding, towels, or furniture.
In some cases, an animal may be a source of infestation.
How Is Scabies Diagnosed?
Your medical history, physical examination of the affected areas, and skin scraping diagnose scabies. During a skin scraping, a small skin sample is scraped off with a scalpel and placed in mineral oil under a microscope to look for mites and eggs.
Your doctor may also use a black light to detect tell-tale signs of infestation, such as mite droppings or eggs.
Scabies Treatment
Treatment for scabies involves using topical medications to kill the mites and eggs. The most commonly prescribed medications are permethrin cream and crotamiton lotion, which can be safely used in children two months or older.
Your doctor may also prescribe oral ivermectin if your infestation covers a large area, if you have had difficulty controlling the infestation with topical medications, or if your case is severe.
5. Measles

Measles is a highly contagious viral infection that can cause fever, rash, and other symptoms. It is spread through close contact with an infected person or through contact with respiratory secretions such as saliva or nasal discharge.
Measles is preventable through immunization, which most children receive at 12 to 15 months and again at four to six years of age. Vaccination is the best protection against measles and its complications.
What Causes Measles?
Measles is caused by the highly contagious measles virus, which is part of the family of paramyxoviruses. The virus spreads through direct contact with an infected person or contact with respiratory secretions.
It can also be spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Measles is most contagious before, during, and after a rash appears.
How Is Measles Diagnosed?
Measles is usually diagnosed based on the patient’s symptoms and a physical examination. If the diagnosis is uncertain, laboratory tests such as a blood test or throat swab can be used to confirm the presence of the measles virus in the body.
Measles Treatment
Treatment for measles typically focuses on relieving symptoms as the body fights off the virus. This may include staying home, drinking fluids to prevent dehydration, and taking over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen to reduce fever and aches.
In some cases, a doctor may also prescribe antiviral medications to help reduce the severity of symptoms. Vaccination is the best way to protect against measles and other related illnesses.
6. Heat Rash

Heat rash, also known as prickly heat, is a skin condition that occurs when sweat gets trapped in the skin and causes irritation. It usually appears as small red bumps or patches in areas of the body that are prone to sweating, such as the neck, armpits, and groin area.
Heat rash is most commonly seen during hot weather, but it can occur anytime. Treatment typically involves keeping the affected area cool and dry while avoiding irritants such as perfumes or scented body washes.
What Causes Heat Rash?
• Prolonged exposure to hot, humid weather
• Wearing tight clothing that traps sweat
• Applying lotions or creams that contain alcohol or other irritating ingredients
• Using heavy blankets on the body during sleep
• Engaging in strenuous activities which cause increased sweating
How Is Heat Rash Diagnosed?
Heat rash is typically diagnosed through observation by a healthcare professional, who will look for the tell-tale red bumps or patches.
A doctor may ask about the patient’s symptoms and recent activities to determine the cause of the heat rash and provide appropriate treatment.
In some cases, a skin biopsy may be taken to rule out other possible causes, such as an infection.
Heat Rash Treatment
Treatment of heat rash typically involves avoiding further exposure to the irritant and allowing the skin to cool. Common treatments include:
• Keeping the affected area dry and cool
• Applying a cool compress such as a wet cloth or ice pack to the affected area
• Taking cool baths with oatmeal or baking soda to reduce itching
• Applying moisturizers, creams, or lotions that contain calamine or hydrocortisone
• Avoiding tight-fitting clothing
• Using good hygiene practices, such as changing out of sweaty clothes after exercise
7. Ringworm

Ringworm is a fungal infection affecting skin, hair, and nails. It is highly contagious and spreads through contact with an infected person or animal and shared objects like towels and clothes.
The condition can be treated with antifungal creams and ointments, available over the counter or by prescription. In severe cases, oral medications may be necessary for treatment.
Common symptoms of ringworm include red, raised patches on the skin that have flaky or scaly edges.
What Causes Ringworm?
A type of fungus called dermatophytes typically causes ringworm. These fungi live on the skin’s surface and thrive in moist, warm environments.
Ringworm can be spread through contact with an infected person or animal and through sharing objects like towels, clothes, and combs.
Additionally, walking barefoot in public areas, such as locker rooms and public showers, can increase the risk of contracting ringworm.
How Is Ringworm Diagnosed?
Ringworm is usually diagnosed based on the appearance of its rash. To confirm a diagnosis, a doctor may take a sample of skin cells to check for fungi under a microscope.
Additionally, they may order specific tests, such as a KOH exam or culture test, to rule out other conditions that produce similar rashes.
Ringworm Treatment
Depending on the ringworm infection’s severity, the doctor may recommend medications and lifestyle changes to treat the infection. Some topical medications like antifungal creams, ointments or gels may be used.
The infected person may also be asked to disinfect their surroundings by washing bedding and clothes daily and wearing loose clothing around affected areas.
8. Scarlet Fever

Scarlet Fever is an infection caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pyogenes. It typically affects children between the ages of 5 and 15 and is characterized by a sore throat, fever, and a red rash that covers most of the body.
Scarlet Fever can lead to severe complications, including ear infections, rheumatic fever, and kidney inflammation. Treatment usually involves antibiotics such as penicillin or other medications to reduce symptoms.
What Causes Scarlet Fever?
Scarlet Fever is caused by a bacterium known as Streptococcus pyogenes.
The bacteria is passed from person to person via air droplets or through contact with an infected person’s saliva, mucus, and skin infections.
Sleeping in the same bed, sharing toys, eating utensils, and towels can all expose you to these bacteria and lead to infection.
How Is Scarlet Fever Diagnosed?
Scarlet Fever is usually diagnosed based on symptoms such as a sore throat and rash. A doctor may also take a sample from the back of your throat to test for bacteria.
If the infection is severe, they may suggest other tests, such as blood tests or imaging scans, to check for complications.
Scarlet Fever Treatment
Scarlet Fever is usually treated with antibiotics, which will help to stop the infection from spreading and reduce the symptoms.
It’s important to finish taking all of your prescribed medication, even if you start feeling better before you finish it.
To relieve the symptoms of Scarlet Fever, drink plenty of fluids, rest, and take ibuprofen or paracetamol if necessary.
9. Roseola

Roseola is a common childhood illness caused by a virus. Symptoms usually develop around 3 to 5 days after exposure and may include a high fever, which lasts for around three to five days, followed by a body rash that appears as pink or red spots on the chest and abdomen.
What Causes Roseola?
A virus causes roseola, usually the human herpes virus 6 or 7. It is most common in infants and young children and can be transmitted through contact with bodily fluids from an infected person.
It can also spread through coughing and sneezing. Roseola is not considered to be very contagious, and it does not cause any long-term health problems.
How Is Roseola Diagnosed?
Roseola is usually diagnosed based on its distinctive symptoms. A doctor may also order a blood test to help confirm the diagnosis, but this is not always necessary.
The rash typically appears 3-5 days after the onset of fever and fades after a few days. A doctor may order further tests to rule out other illnesses if there is doubt.
Roseola Treatment
There is no specific treatment for roseola, as it will usually resolve on its own. The most important thing is to ensure that the child remains well-hydrated and comfortable until the fever and rash have passed.
In some cases, a doctor may prescribe an anti-fever medication to help reduce discomfort. It is also important to keep the child away from other people to avoid spreading the virus.