The Effects of Crash Dieting on Your Body: 10 Things You Need to Know
Crash dieting is a rapid weight loss method with many health consequences and a common practice among many who aim to shed pounds quickly. Ideally, any weight loss regimen needs professional guidance and emphasizing long-term, sustainable health benefits.
This article highlights the significant effects of crash dieting on the body, providing a comprehensive understanding that extends beyond the allure of quick results.
Muscle Loss

Crash diets cause a rapid weight reduction, but most of this loss is water weight and muscle rather than fat, particularly true for very low-calorie diets, typically containing less than 800 calories daily. The decrease in muscle mass is detrimental to strength levels and physical performance, making everyday tasks like carrying groceries or climbing stairs more challenging.
Dehydration
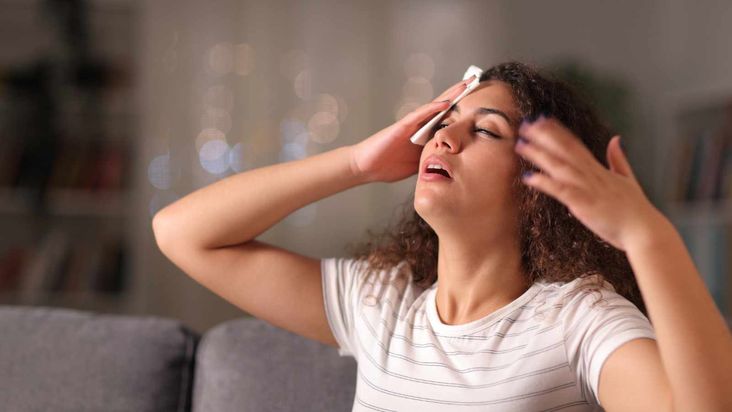

Your body relies on water to stay hydrated and balanced. Restricting your caloric intake can lead to dehydration due to insufficient fluid intake. Depending on a person’s fitness goals, drinking adequate fluids during weight loss is essential to avoid dehydration and its associated side effects, including dizziness and fatigue.
Weak Immune System
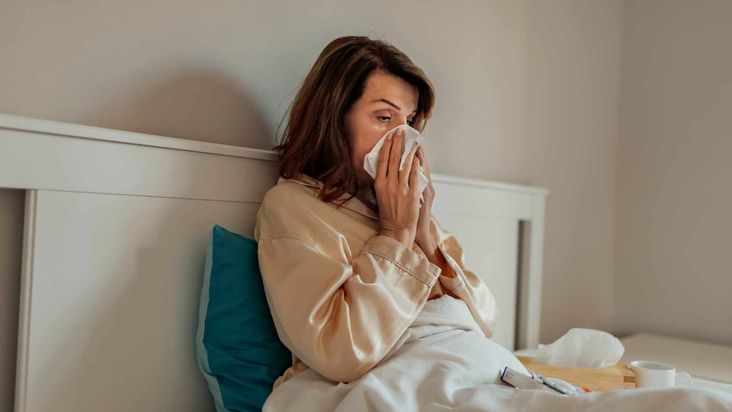

Crash diets can weaken the immune system because diets that are extremely low in calories and vital nutrients can cause your body to become malnourished, making it difficult to fight off infections or illnesses caused by bacteria or viruses.
Heart Issues
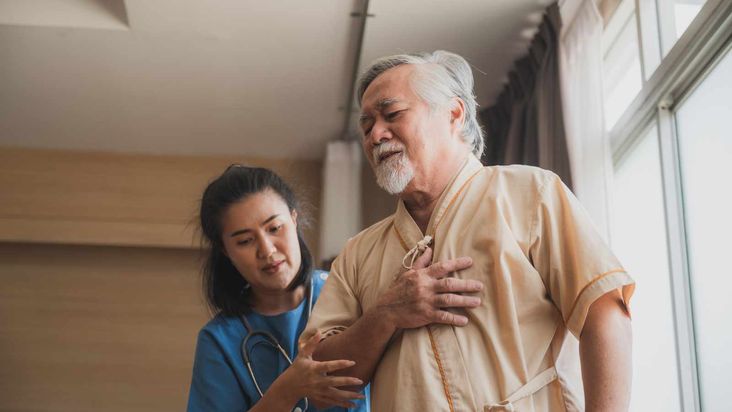

Unhealthy crash diets can harm heart health, depriving the body of essential nutrients required for maintenance and repair. Also, low-calorie diets can elevate the risk of developing arrhythmias, hypertension, and cardiac arrest. Prioritize a balanced and nourishing approach to eating for long-term well-being and cardiovascular health.
Low Energy
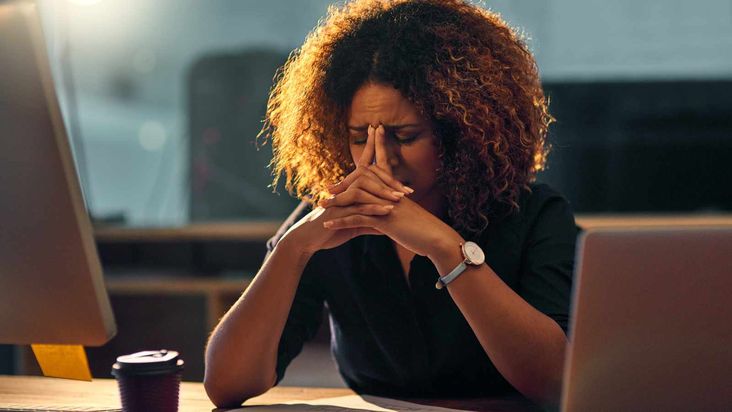

Crash diets cause fatigue and low energy levels as the body lacks the necessary vitamins and minerals. Eating nutritious whole foods is essential for providing your body with the fuel it needs for energy throughout the day, so ensure you get enough calories from nutrient-rich sources like lean meats, complex carbohydrates, fruits, seeds, nuts, and vegetables.
Slow Metabolism

Engaging in crash dieting can hinder your metabolism. When your body is in a caloric deficit and lacks vital nutrients, it conserves energy. Continuously crash dieting will lead to weight regain, as your metabolism slows significantly due to repeated food intake restrictions. Establish regular eating patterns that prioritize nutrient-dense meals.
Ketone Production

When the body lacks carbohydrates, it produces ketones, leading to headaches and nausea. Ketones are created when fat is burned for energy, resulting in ketosis, where the body uses fat stores instead of glucose for fuel. While it benefits people with diabetes, those without it should not attempt ketosis as a quick weight-loss solution.
Bad Skin
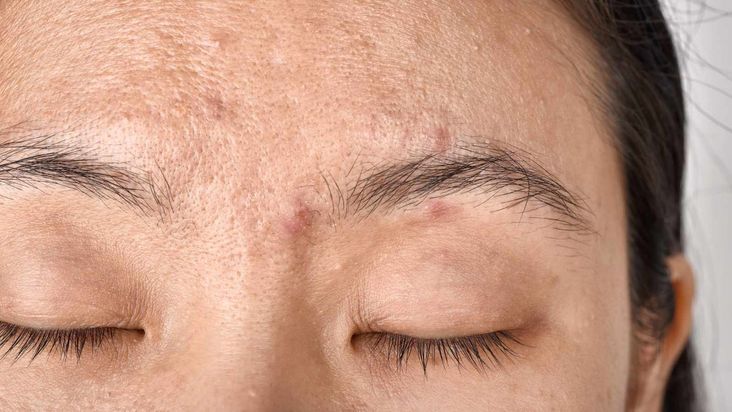
Crash dieting can cause wrinkles, dryness, and uneven skin tones. The skin comprises collagen and elastin, proteins that need vitamin C to produce. If your diet lacks vitamins or minerals, collagen production will be hindered, resulting in a greater risk for premature wrinkles.
Mood Swings

Extreme diets can trigger mood swings due to nutrient deficiencies, prolonged hunger, and feelings of deprivation. Persistent dieting can induce guilt and anxiety, so obtaining sufficient nutrients from nutrient-dense sources and cultivating mindful eating habits is essential.
Hair Loss
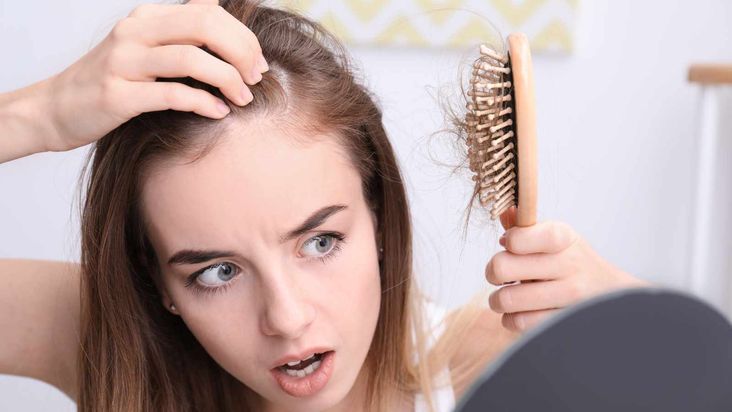

Crash diets deprive the body of essential nutrients, including proteins, vitamins, and minerals required for healthy hair, leading to low density, breakage, dullness, and balding. Consume adequate protein from legumes, lean meat sources, nuts, and dairy products to promote thicker hair growth.